- The best sleeping position for breathing problems depends on the underlying causes of your symptoms — such as sleep apnea, COPD, asthma, and heart disease.
- Sleeping on your side allows for improved airflow, as it can help reduce pressure on your airway, making it easier to breathe and fall asleep.
- Oura features that can help you improve sleep quality when you’re dealing with breathing issues include Blood Oxygen Sensing (SpO2) and Nighttime Movement.
Chances are, you have a preferred sleeping position that brings comfort and zzz’s to your nights. However, if you are experiencing breathing problems, such as a cold or a medical condition like obstructive sleep apnea, you may find it challenging to find a comfortable sleeping position.
If breathing problems are disturbing your sleep, it can lead to further health issues associated with poor sleep. Finding the best sleeping position for breathing problems is a crucial step toward alleviating this issue.
How Breathing Problems Affect Oxygen Levels
Breathing problems at night can do more than disrupt sleep — they can also lower your blood oxygen levels. When airflow is restricted, less oxygen enters your bloodstream, which can leave you waking up tired, impact recovery, and increase long-term health risks. This is why many experts talk about finding the best sleep position to increase oxygen levels, especially if you live with conditions like sleep apnea, COPD, or asthma.
Oura can help you track these changes. The Blood Oxygen Sensing (SpO₂) feature measures your nighttime oxygen saturation and breathing regularity, giving you insights into whether your sleep position or other factors might be affecting your airflow. By pairing this data with your Sleep Score, you can better understand how breathing impacts your rest — and make adjustments like changing your sleep position to improve both oxygen levels and sleep quality.
What Are the Best Sleeping Positions for Breathing Problems?
The best sleeping positions for breathing problems are those that improve airflow and help keep your oxygen levels steady, with side sleeping often recommended as the top choice.
Sleeping on Your Side
Sleeping on your side allows for improved airflow. The reason: Gravity pulls your tongue toward your cheek instead of the back of your throat, reducing pressure on your airway and making it easier to breathe and fall asleep.
This sleeping position has been shown to reduce breathing problems for people with sleep apnea, a sleeping disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. Sleeping on the side has also been shown to reduce snoring — a common sleep apnea symptom — and it has even been suggested as a major treatment intervention for the condition.
Additionally, side sleeping in the fetal position is usually the most comfortable position for pregnant people, plus it helps reduce back pain.
READ MORE: The Best Sleeping Position for Lower Back Pain
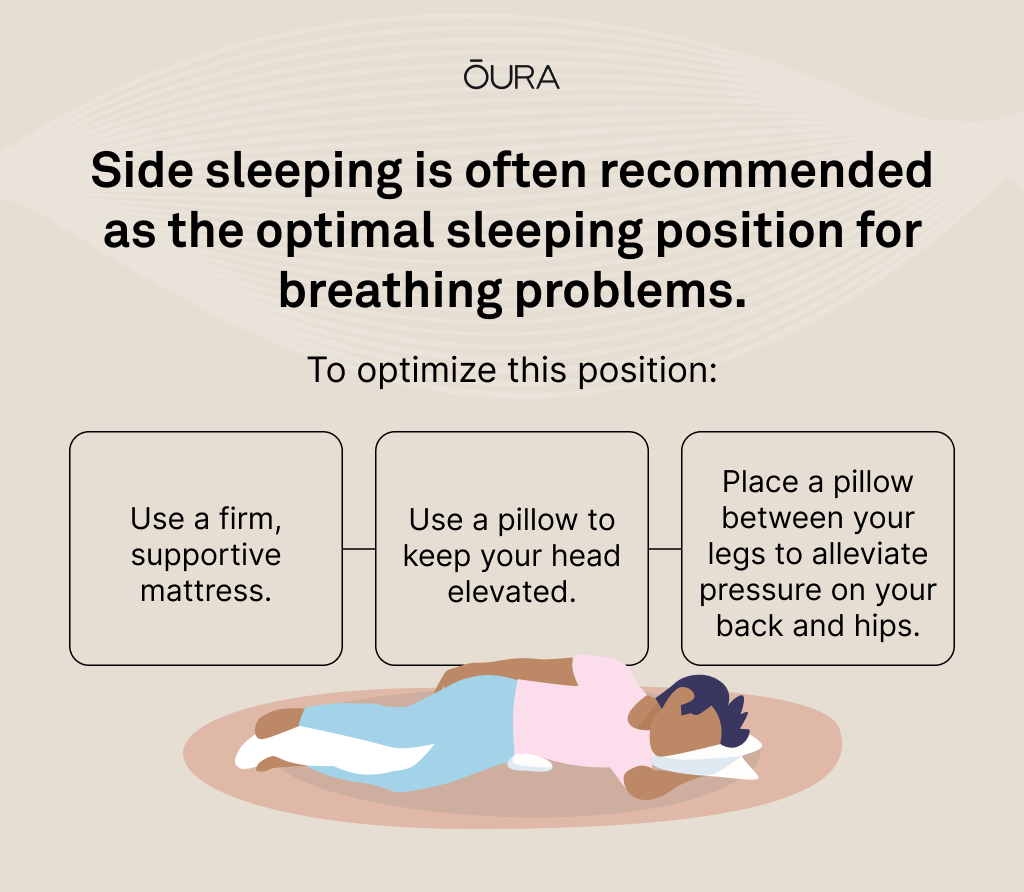
Considerations: Sleeping on your side might cause neck and shoulder pain for some people. Use a firm mattress that offers the right amount of support for spinal alignment. You can also support your head with a pillow and place a pillow between your legs to reduce pressure on your back and hips.
Sleeping on Your Stomach
Sleeping on your stomach can take the weight of your heart and large blood vessels off your lungs, allowing them to expand fully and making breathing easier. In fact, during the COVID-19 pandemic, healthcare providers discovered that placing patients in a prone position during recovery improved breathing.
Stomach sleeping can increase oxygen supply and reduce breathing issues among people with sleep apnea.
Considerations: When sleeping on your stomach, consider using a mattress that provides spinal support. You can also use a pillow to support your head while leaving room to breathe properly.
What Sleeping Positions Should You Avoid with Breathing Problems?
The sleeping position most often linked with worse breathing and lower oxygen levels is back sleeping, which can obstruct the airway and worsen conditions like sleep apnea. For instance, it’s been shown to worsen breathing problems in people with sleep apnea. This is because, in the supine position, your tongue, soft tissue, and jaw are likely to fall back toward your throat, thereby obstructing the airway and increasing breathing difficulties.
In one study, the apnea index was found to be twice as high during time spent sleeping on the back compared to time spent sleeping on the side. Moreover, sleeping on your back can also increase snoring and gastroesophageal reflux (GERD).
Considerations: If you prefer sleeping on your back, you can minimize breathing problems by using a pillow to keep your head elevated. This may also improve snoring and minimize the risk of acid reflux. Placing a pillow under the knees can also reduce the risk of spinal misalignment, which can cause shortness of breath.
RELATED: 8 Popular Sleeping Positions & What They Mean for Your Health
What Conditions May Impact Your Breathing?
While studies often suggest sleeping on your side as a remedy for breathing problems, keep in mind that the ideal sleeping position for breathing problems varies based on the underlying causes of your symptoms.
Besides obstructive sleep apnea, there are several other health conditions that can make breathing difficult when you’re lying down or sleeping.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
COPD affects an estimated 328 million people worldwide. It primarily targets the airways and lungs, hindering the body’s ability to get oxygen. As a result, COPD often leads to symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath, which disrupt sleep.
Most people with COPD typically try to sleep on their side. This position can take pressure off your lungs and improve airflow, making it easier to fall and stay asleep.
Asthma
Asthma causes airways to narrow and swell, which makes it difficult to breathe. Studies suggest that sleeping on your back with your neck and shoulders elevated or sleeping on your left side can alleviate asthma symptoms.
However, it’s important to avoid sleeping on your right if you have asthma. Sleeping in this position has been found to increase resistance in the lung passages, which causes and worsens breathing difficulties.
 Heart Conditions
Heart Conditions
Shortness of breath is one of the common symptoms of heart conditions, such as heart failure and heart attacks. When your heart is not working as well as it should, it won’t be able to pump oxygenated blood efficiently. Furthermore, poor heart function can cause fluid build-up in the lungs, causing breathing difficulties.
If you have a heart condition, you want to avoid sleeping on your left side as this will put pressure on your heart. Rather, opt for sleeping on your right side or on your back.
Although not a diagnostic tool, Oura Ring can help you keep track of your heart rate and heart rate variability (HRV), which are both critical to your heart health.
READ MORE: How Oura Data Supported These Members in Noticing Critical Health Changes
Anxiety
When you’re anxious, your body releases hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol. These hormones can cause a number of physical changes, including increased heart rate, breathing rate, and muscle tension, all of which can make breathing difficult. Anxiety can also make you hyperventilate, which is a type of rapid, shallow breathing.
Side sleeping, particularly in the fetal position, often works well for people with anxiety because it’s comforting. Lying on your back in the starfish position can also help relieve anxiety. This sleeping position stretches your body, thereby increasing blood flow and allowing for improved sleep.
READ MORE: How Anxiety Affects the Brain—Plus 3 Science-Backed Ways to Manage It
Allergies
Over 100 million people in just the U.S. experience allergies every year. Allergies are caused by an overreaction of the immune system to a harmless substance, such as pollen and dust. Allergic reactions can cause inflammation in the airways, which can make it difficult to breathe. Allergies can also trigger asthma attacks, which are characterized by wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
When you have allergies, lying flat on your back can worsen congestion. You should elevate your head with pillows or sleep on your side to help keep your airway open.
Apart from these conditions, some environmental factors may also contribute to breathing issues and make it difficult to get optimal sleep:
- Air pollution: Air pollution can contain a variety of harmful pollutants, such as particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide. These pollutants can irritate the airways and make it difficult to breathe.
- Changes in temperature and humidity: Extreme temperatures and humidity can make it difficult to breathe, especially for people with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
- High altitude: High altitude can cause low oxygen levels, which can make it difficult to breathe.

How to Improve Overall Sleep Quality
Finding the ideal sleeping position for breathing problems will go a long way in ensuring that you get a good night’s sleep, but you can also get better sleep in several other ways:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your lungs, making it harder to breathe. Conversely, losing weight can enhance your breathing and sleep quality.
Member Story: Oura can support you in your weight loss journey, as evidenced by Bailey C. With the help of Oura data, Bailey successfully balanced getting quality sleep and staying active to achieve an impressive 110-pound weight loss. - Get regular exercise. Exercise helps to strengthen your respiratory muscles and improve your overall lung function. However, it is important to avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as this can make it difficult to fall asleep.
- Create a relaxing bedtime routine. A relaxing bedtime routine can help you to wind down and prepare for sleep. This may include taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to calming music.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed. Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep, so it is best to avoid them in the hours leading up to bedtime. Oura members can use Tags to identify how bad sleep habits, such as alcohol and caffeine consumption before bed, affect sleep quality and readiness to take on the day’s stressors.
- Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Light can suppress the production of melatonin, a hormone that helps to regulate sleep. Noise can also disrupt sleep, so it’s important to create a dark and quiet environment in your bedroom. A cool temperature is also ideal for sleep.
- Treat your underlying breathing condition. If you have a breathing condition such as asthma, COPD, or sleep apnea, it’s important to seek medical advice for effective treatment. This will help to reduce your breathing problems and improve your overall health.
FAQs About Sleep Position and Breathing
What is the best sleep position to increase oxygen levels?
The best sleep position to increase oxygen levels is usually sleeping on your side, because it helps keep the airway open and reduces obstructions that can lower oxygen during the night.
Is sleeping on your stomach good for breathing problems?
Yes, stomach sleeping (prone position) can improve lung expansion and oxygen intake, but it may cause strain on the spine without proper pillow support.
Why does sleeping on my back make breathing harder?
When you sleep on your back, your tongue and soft tissues can fall toward the throat, narrowing the airway and making it harder to breathe. This is why back sleeping often worsens sleep apnea and snoring.
Can sleep position help with sleep apnea?
Yes, side sleeping has been shown to reduce symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea, including snoring and nighttime oxygen drops. Some people even use special pillows or devices to encourage side sleeping.
How can Oura Ring help if I have breathing problems at night?
Oura’s Blood Oxygen Sensing (SpO₂) feature measures nighttime oxygen levels and breathing regularity, helping you see if your sleep position or other factors may be affecting your airflow and overall sleep quality.




